2026 Top Motorized Valve Types and Their Applications?
In the evolving landscape of industrial automation, the significance of Motorized Valves cannot be overstated. These devices control fluids with precision, enhancing system efficiency. As industries advance, so do the types of Motorized Valves available, each catering to specific applications.
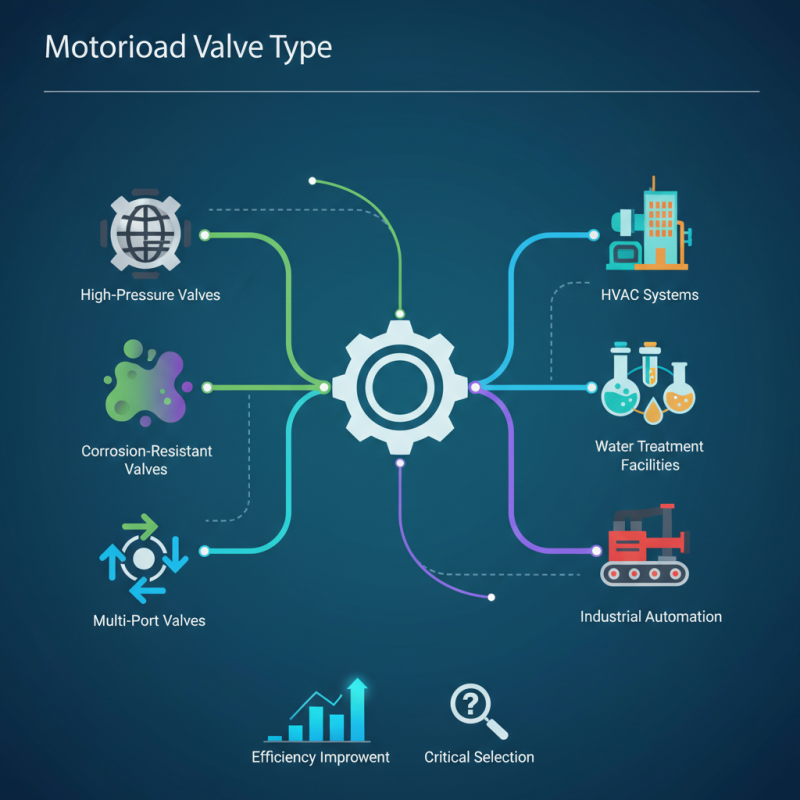
Understanding the various Motorized Valve types is crucial. Some may excel in high-pressure environments, while others are designed for corrosive substances. Each valve comes with its own unique benefits and drawbacks. There is a real need to analyze and choose wisely. This choice impacts overall operational efficiency.
Beyond just functionality, the applications of Motorized Valves span numerous fields. From HVAC systems to water treatment facilities, the versatility is impressive. However, one must reflect on their selection process. Is the chosen valve right for the task? Are there potential risks overlooked? These questions are vital as industries strive for improvement.
Overview of Motorized Valves and Their Importance in Industrial Applications
Motorized valves play a crucial role in various industrial settings. They automate the control of fluids, reducing manual labor and enhancing efficiency. These valves can regulate flow, pressure, and temperature with precision. In many processes, their reliability is vital. Operators need to trust that these components work correctly.
Despite their importance, motorized valves are not without flaws. Proper maintenance is essential. If neglected, they may malfunction, leading to costly downtime. Additionally, installation and calibration require skilled technicians. Poorly executed setups could cause leaks or operational failures. Industries must invest time in training to ensure effective use.
The versatility of motorized valves is evident. They find applications in HVAC, water treatment, and chemical processing. Each sector has unique requirements. A valve suitable for one application may not perform well in another. Assessing specific needs is crucial for optimal performance. Understanding these dynamics can lead to a more efficient system overall.
Types of Motorized Valves: A Comprehensive Classification Guide
Motorized valves play an essential role in various industries. They control the flow of liquids and gases. This includes sectors like HVAC, water treatment, and chemical processing. According to a recent report from MarketsandMarkets, the motorized valve market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% between 2021 and 2026. Different types of motorized valves cater to specific applications, making understanding their classification crucial.
There are several main types of motorized valves. Electric actuated valves offer precise control. They are suited for applications requiring quick opening and closing. Pneumatic valves excel in high-speed operations. Conversely, hydraulic valves are often preferred where heavy-duty performance is necessary. However, the choice can be challenging. Factors such as environment, pressure, and type of fluid can complicate decision-making. Some applications might misuse these types, leading to inefficiencies or failures.
In fluid systems, ball and butterfly valves are common. Ball valves ensure tight sealing and quick operation. Butterfly valves, while space-saving, may not offer the same pressure handling. The choice depends on operational needs. Misapplications can stall projects and increase costs. Thus, professionals must carefully evaluate each valve type to optimize performance and reliability.
Key Applications of Different Motorized Valve Types in Various Industries
Motorized valves have found essential roles across multiple industries. Their applications range from water management to HVAC, and even in food processing. Data from industry reports indicates that the global motorized valve market is expected to grow significantly, driven by a push for automation. For instance, in the oil and gas sector, precise control is vital. Motorized ball valves provide that control, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
In wastewater treatment, motorized valves regulate flow to prevent system overloads. Automatic control can enhance operational efficiency by up to 30%. This is crucial in managing environmental impacts and ensuring compliance with regulations. However, the integration process can face challenges. Misalignment or incorrect installation can lead to valve failures, disrupting entire systems.
Tips: Regular maintenance checks can prevent failures. Monitor the operational status of valves frequently. Training staff on proper usage can also reduce errors in operation. Ensuring the right type of motorized valve is selected for each application is paramount. The right choice improves system reliability and efficiency. For industries adapting to automation, understanding valve mechanics is essential. It can be the difference between seamless operations and costly downtime.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Motorized Valves for Specific Uses
When selecting motorized valves, several factors are crucial. Understand your system's requirements. Each application may need specific valve types. Temperature, pressure, and flow rate are vital considerations. The environment also plays a large role. For example, corrosive environments demand specially coated valves.
Tips: Always check the compatibility of valve materials with the fluid. This prevents unexpected failures.
Actuator type is another important aspect. Electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuators have different advantages. Electric actuators might simplify installation. Pneumatic options can deliver faster responses. Evaluate the actuation speed required for your application.
Tips: Analyze how often the valve will operate. This can inform your choice of actuator type and maintenance requirements.
It's also essential to consider control methods. Some applications require precise control, while others may not. Budget constraints may limit your options. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term costs. Look for options that offer longevity and reliability.
Future Trends and Innovations in Motorized Valve Technology
The realm of motorized valves is poised for transformation. Future trends reflect significant advancements in smart technology. According to a recent market analysis, the global motorized valve market is projected to reach USD 8.7 billion by 2026. This growth stems from increased automation in various industries, emphasizing efficiency and reliability.
Innovations like IoT integration are making waves. Sensors and data analytics enhance real-time monitoring. This enables predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and costs. However, challenges persist. Many industries struggle with retrofitting old systems. Transitioning to new technologies is often met with resistance.
In a survey, 45% of companies reported barriers in adopting smart valves. The need for training and adaptation cannot be overlooked. Moreover, the complexity of installation may hinder progress. The balance between innovation and implementation must be carefully considered to ensure seamless integration. Such factors shape the future landscape of motorized valve applications.
